- Product Name
- CasNo
- MF
- MW
- Content
- Appearance
- Packing
- Apply
- Vandetanib
- 443913-73-3
- C<sub>22</sub>H<sub>24</sub>BrFN<sub>4</sub>O<sub>2</sub>
- 475.361
- Yellow solid
Your Location:Home > Products > API&Intermediates > Vandetanib

|
Anticancer drugs |
Vandetanib is a kind of small molecule multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor studied and developed by the British AstraZeneca Company. In April 2011, it was approved the US FDA for entering into market under the trade name Zactima. The drug, as a tablet, can be applied to the treatment of advanced medullary thyroid cancer of adult patients. Vandetanib is a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and belongs to the Anilinoquinazoline compounds, called "second generation Iressa”. It not only acts on the tumor cells, EGFR, VEGFR and RET tyrosine kinases, but can also inhibit other kind of tyrosine kinases and serine/threonine kinases. Vandetanib is the first approved drugs approved for treatment of medullary thyroid carcinoma. It is suitable for treating unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic-symptoms or progressive medullary thyroid carcinoma. A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial results have showed that vandetanib can significantly delay the progression time of locally advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer. The recommended daily dose is 300 mg (oral), when the patient exhibits tolerance to drugs or being not able to tolerate the toxicity, they should stop treatment immediately. Those most common adverse reactions of this medicine include diarrhea, rash, acne, nausea, hypertension, headache, fatigue, loss of appetite and abdominal pain. The adverse reactions is dose-related; at <300 mg/d, the patient has a well tolerance with the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) being 300mg. There are many kinds disease types contained in the Ⅱ phase clinical study. The NSCLC clinical trials of vandetanib are currently under way for China. British AstraZeneca Company, in May 2001 and October 2001, respectively, had obtained preferential access to the world's patent (WO2001032651, WO 2001074360) and applied corresponding protection on the formula, synthesis methods and pharmaceutical compositions of these compounds (including bonus salt). Vandetanib can inhibit the development of medullary thyroid carcinoma, and is the first FDA-approved drug for the treatment of the disease and will provide support for the treatment of advanced medullary thyroid cancer in adult patients. The above information is edited by the lookchem of Dai Xiongfeng. |
|
Treatment of advanced (non-small cell lung cancer) NSCLC |
A study published in the [Journal of Clinical Oncology] have showed that compared with gefitinib which only has inhibitory effect on EGFR, vandetanib can effectively extend the progression-free survival period of the non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. In this phase II clinical trial conducted by doctors Ronald B. Natale from Los Angeles Cedars-Sinai Cancer Center, clinical study compared the treatment efficacy of vandetanib (300 mg/d) and gefitinib (250mg/d) on 168 cases of NSCLC patients who had been subject to failing first-line or second-line chemotherapy. Compared with gefitinib, vandetanib significantly increased efficiency and prolonged the progression-free survival, period respectively, by 8% and 1%, 11.9 weeks and 8.1 weeks, (P = 0.011). In clinical trials, if there is progression of the disease or if the patient can’t tolerate the toxicity, they allowed the patients to change the treatment regimen. Experimental results had shown that using gefitinib for replacing vandetanib in patients gave a disease control rate of 14% while using vandetanib to replace gefitinib gave a disease control rate of 32%. The overall survival period in the case of vandetanib → gefitinib was 6.1 months while it was 7.4 months in the cases of gefitinib → vandetanib. |
|
Preparation method |
Use 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-benzoic acid ethyl ester as a starting material, go through substitution, reduction, nitrification, reduction, cyclization aromatization to give 4-chloro-6-methoxy--7-(N-methyl piperidin-4-ylmethoxy) quinazoline (A), A was then reacted with 4-bromo-2-aniline to obtain the targeted compound vandetanib. |
|
Synthesis |
Vandetanib contains a 4-anilinoquinazoline scaffold similar to other EGFR inhibitors, and the synthesis described below is based on a recent patent (Scheme).Commercially available vanillic acid (262) was treated with benzyl bromide, DIPEA and Et3N to give ethereal ester 263 in 93% yield. Arene 263 was then subjected to nitration conditions to provide nitroarene 264 in 86% yield, which underwent immediate reduction with sodium dithionite in acetonitrile and water to give aniline 265 in 92% yield. Aniline 265 was then treated with foramidine acetate in isobutanol which affected an intramolecular cyclization reaction, giving rise to dihydroquinazolin-4-one 266 in 98% yield. Heterocycle 266 was treated with phosphorous oxychloride and the resulting quinazoline chloride was subsequently reacted with 4-bromo-2-fluoroaniline 267 and trifluoroacetic acid to give hydroxyaniline 268 in 90% for the three-step sequence. Phenolic azacycle 268 was then alkylated with sulfonate 269 to furnish piperidine 270 in 77% yield. Subsequent treatment with formic acid and aqueous formaldehyde under elevated temperatures gave vandetanib (XXIII) in 91% yield. |
|
Drug interactions |
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Analgesics: possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with methadone - avoid. Anti-arrhythmics: possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with amiodarone or disopyramide - avoid. Antibacterials: possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with parenteral erythromycin and moxifloxacin - avoid; concentration reduced by rifampicin - avoid. Antihistamines: possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with mizolastine - avoid. Antimalarials: possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with artemether with lumefantrine - avoid. Antipsychotics: possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with amisulpiride, chlorpromazine, haloperidol, pimozide, sulpiride and zuclopenthixol - avoid; avoid concomitant use with clozapine, risk of agranulocytosis. Beta-blockers: possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with sotalol - avoid. Cytotoxics: possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with arsenic trioxide - avoid. Hormone antagonist: possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with toremifene - avoid. 5HT3 -receptor antagonists: possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with ondansetron - avoid. Pentamidine: possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias - avoid. |
|
Metabolism |
N-desmethyl-vandetanib is primarily produced by CYP3A4, and vandetanib-N-oxide is primarily produced by flavin-containing monooxygenase enzymes FMO1 and FMO3. Unchanged vandentanib and metabolites vandetanib N-oxide and N-desmethyl vandetanib were detected in plasma, urine (25%) and faeces (44%). |
|
Brand name |
Zactima (AstraZeneca);Caprelsa. |
InChI:InChI=1/C22H24BrFN4O2/c1-28-7-5-14(6-8-28)12-30-21-11-19-16(10-20(21)29-2)22(26-13-25-19)27-18-4-3-15(23)9-17(18)24/h3-4,9-11,13-14H,5-8,12H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26,27)
The invention discloses tyrosine kinase ...
Vandetanib is an orally available tyrosi...
Vandetanib (ZD6474) and its chlorine ana...
A novel strategy to prepare 4-anilinoqui...
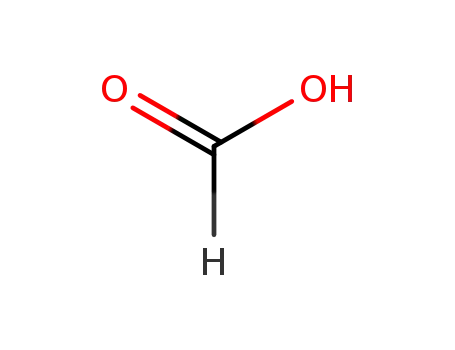
formic acid
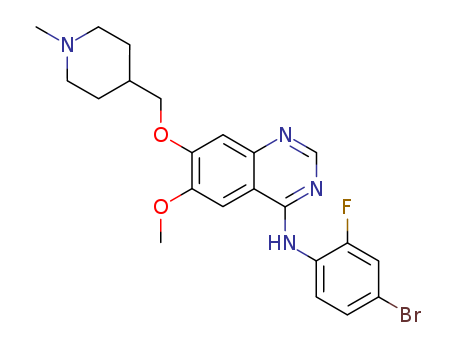
N-Desmethylvandetanib

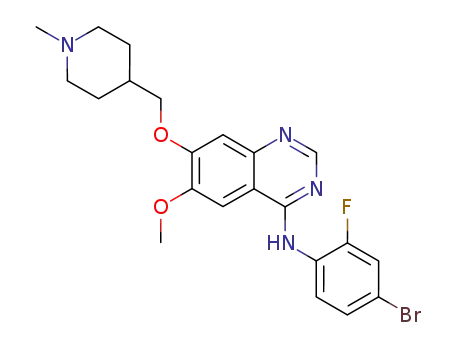
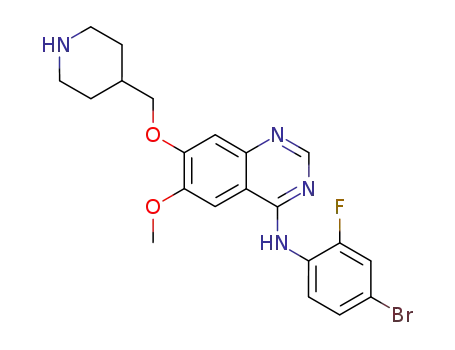
vandetanib
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
sodium tris(acetoxy)borohydride; acetic acid;
In
methanol; dichloromethane;
at 20 ℃;
for 2h;
|
84% |
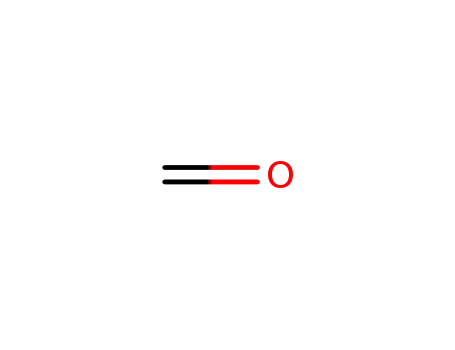
formaldehyd


formic acid

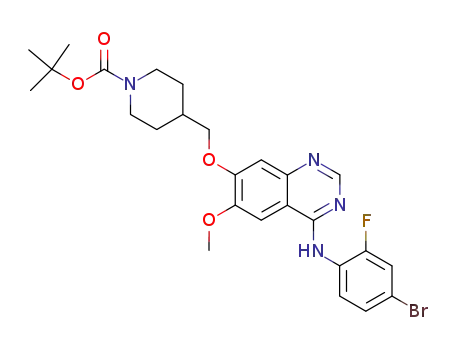
4-(((4-((4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino)-6-methoxyquinazolin-7-yl)oxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester


vandetanib
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
4-(((4-((4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino)-6-methoxyquinazolin-7-yl)oxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester;
With
hydrogenchloride;
In
methanol; water;
at 20 ℃;
formaldehyd; formic acid;
at 20 ℃;
|
78% |
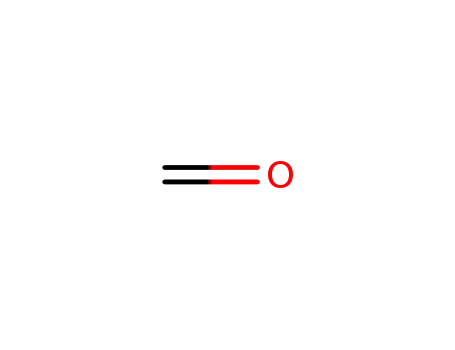
formaldehyd

N-Desmethylvandetanib

4-(((4-((4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino)-6-methoxyquinazolin-7-yl)oxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
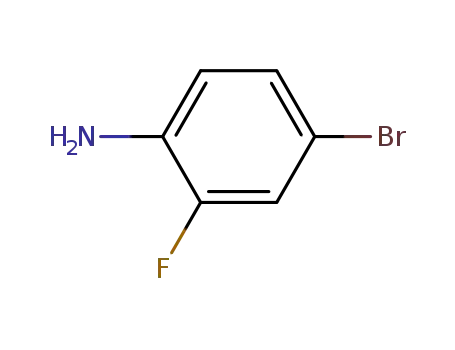
4-bromo-2-fluoroaniline
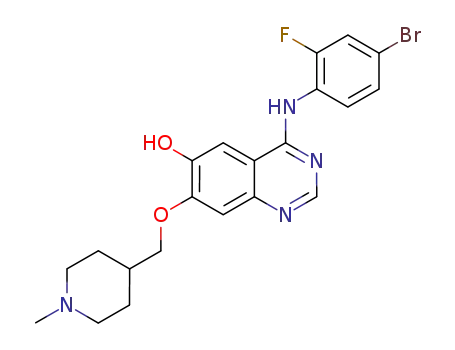
4-((4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino)-7-((1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy)quinazolin-6-ol